Learning objectives for
Module 8
- Upon successful completion of this module, students should be
able to:
- Define key telecommunications concepts & terms.
- Have a broad understanding of the OSI model.
- Be able to present a general design for LAN's & WAN's.
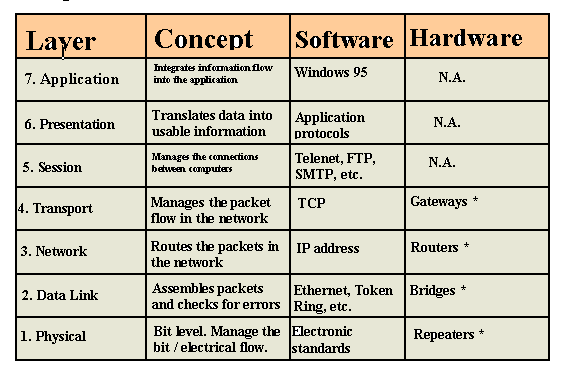
8.1 OSI model.
- The (ISO) International Standards Organization's 7 layer
(OSI)open systems Interconnection reference model for
network comunications. An abstract conceptual model.
- All vendor network products (hardware & software) fit into
the ISO standards.
- The following diagram is a gross simplification of the OSI
Reference Model.
8.2 Some key terms and concepts.
- For communication to take place, you need a media type.
- Radiated Media
- Radio frequency
- Broadcast
- Microwave
- Satellite
- Light frequency
- Infrared
- Conducted Media
- Electrical (less cost, more errors)
- UTP
- Cat 3 LANs up to 10 Mbps
- Cat 4 LANs up to 16 Mmps
- Cat 5 LANs up to 100 Mbps
- Coaxial cable
- Light (more cost, less errors)
- Fiber optic - Very high speed
- PC ports
- Serial
- Parallel
- Connectors
- RJ-11
- RJ-45
- DB-9
- DB-25
- Etc.
- Transmission lines
- Switched
- Leased
- Transmission speeds
- Dial-up (modem)
- 14.4 kbps
- 28.8 kbps (today's standard)
- Faster modems are starting to appear on the market.
- Direct connect
- 56 kbps (fractional T1)
- T1 (DS-1) - 1.5 Mbps
- T2 (DS-2) - 6.3 Mbps (could be fiber)
- T3 (DS-3) - 44 Mbps (usually fiber)
- T4 (DS-3) - 300 Mbps (fiber)
- Etc.
- TCP/IP - the Internet protocol, supports:
- WWW
- Telnet protocol
- FTP
- SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol).
- Etc.
- ATM - the new kid on the block
- LAN protocols
- Ethernet 10BaseT - 10 Mbps
- Fast Ethernet - up to 100 Mbps
- Token Ring - 44.746 Mbps.
- Appletalk
- Etc.
- Signal transfer equipment
- Repeater - just repeats the "bit" signal.
- Bridges - Ethernet bridges pass ethernet data packets
unmolested to the remote side. Most ethernet bridges
filter the 48-bit ethernet addresses, and not IP addresses.
- CSU/DSU - Channel Service Unit/Digital Service Unit.
A device which converts between disparate transmission
protocols or signal formats (e.g., ethernet and T1).
- Routers - Routers look at IP addresses, and decide which
ones to pass through, and which ones to block.
- Gateways - Usually a computer, usually used to transfer
data from one type of network to a different network.
For example, a company with a "private" national network
may have a "gateway" to the Internet.
- Firewall - Generally speaking, a "firewall" is an attempt to
prevent network users from accessing information they
should not access. The more sophisticated the "gateway"
control between your network and the outside world, the
more security you have. The best firewall is a gateway
computer that is specifically programmed to let only
authorized users onto your system.
8.3 LAN's & WAN's.
- There are numerous designs for local area networks (LAN's)
and wide area networks (WAN's)using a wide variety of vendor
hardware and software.
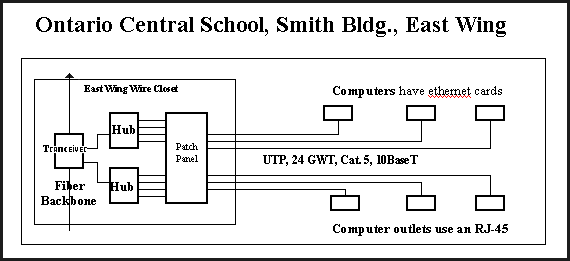
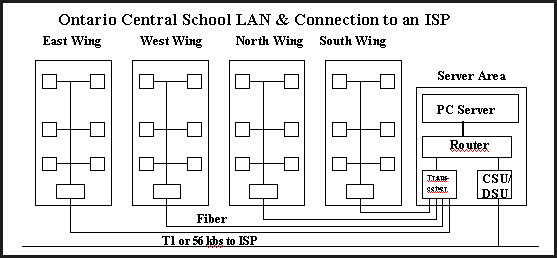
- The following Ontario Central School diagrams are typical
LAN designs.